Market Models and 4 Types of Market Structures. Financial experts bunch enterprises into four particular market models:
- pure competition
- pure monopoly
- monopolistic competition
- oligopoly
Market Models and 4 Types of Market Structures:
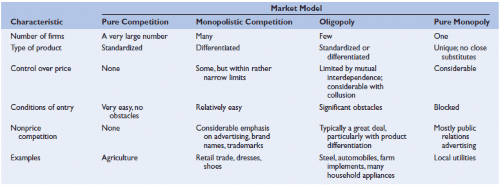
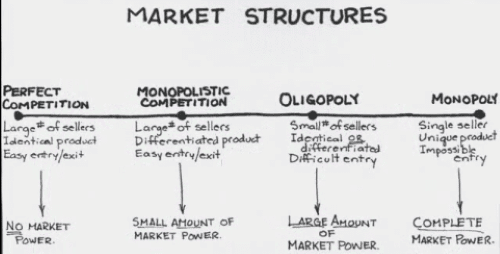
These four market models vary in a few regards: the number of firms in the business, regardless of whether those organizations create an institutionalized item or attempt to separate their items from those of different firms, and how simple or how troublesome it is for firms to enter the business.
Briefly, the four models are as per the following:
PURE COMPETITION MARKET MODELS:
The pure competition includes an expansive number of firms delivering an institutionalized item (that is, an item like cotton, for which every maker’s yield is for all intents and purposes indistinguishable to that of each other maker.) New firms can enter or leave the business effectively.
PURE MONOPOLY MARKET MODELS:
Pure monopoly is a market model in which one firm is the sole merchant of an item or administration (for instance, a nearby electric utility).
Since the passage of extra firms is blocked, one firm constitutes the whole business. The pure monopolist creates a solitary extraordinary item, so item separation isn’t an issue. In this specific market model, price floors are ineffective as sellers are price takers.
Read Also: How to Keep Data Secure in Business? Consider these guidance points!
MONOPOLISTIC MARKET MODELS:
Monopolistic competition is portrayed by a generally vast number of vendors creating separated items (attire, furniture, books).
Display in this model is far-reaching nonprice competition, an offering technique in which a firm does not attempt to recognize its item on the premise of cost yet on qualities like outline and workmanship (an approach called item separation).
Either passage to or, then again exit from monopolistically aggressive enterprises is very simple.
OLIGOPOLY MARKET MODELS:
Oligopoly includes just a couple of merchants of an institutionalized or separated item, so each firm is influenced by the choices of its adversaries and must take those choices into account in deciding its own cost and yield.






















